Treaty Status
About the ATT
The Arms Trade Treaty (ATT), was adopted by the UN
General Assembly to regulate international trade in conventional arms by
establishing the highest international standards and to prevent and
eradicate illicit trade and diversion of conventional arms.
The ATT contributes to international and regional peace, security and stability, reducing human suffering, and promoting cooperation, transparency and responsible action among the international community.
Adoption and entry into force
The ATT was adopted by the UN General Assembly on 2 April 2013 with 154 votes in favour, 3 votes against, and 23 abstentions*. The Treaty opened for signature on 3 June 2013 and entered into force on 24 December 2014 following its ratification, acceptance or approval by 50 states (in accordance with Article 22(1)).
* After the official vote, the delegation of Angola (which had abstained) and Cape Verde (which had not voted) informed the secretariat of the negotiating conference that they had intended to vote in favour of the resolution. Accordingly, 156 States voted in favour of the resolution, 3 voted against it, and 22 abstained from voting.
Status of Participation
118
State Parties*
25
Signatories that are not
yet States Parties**52
States that have not yet joined the treaty
* States that have ratified, accepted, approved or acceded to the treaty
** States that have signed the treaty but not yet ratified, approved, or accepted it
Status of ATT Participation
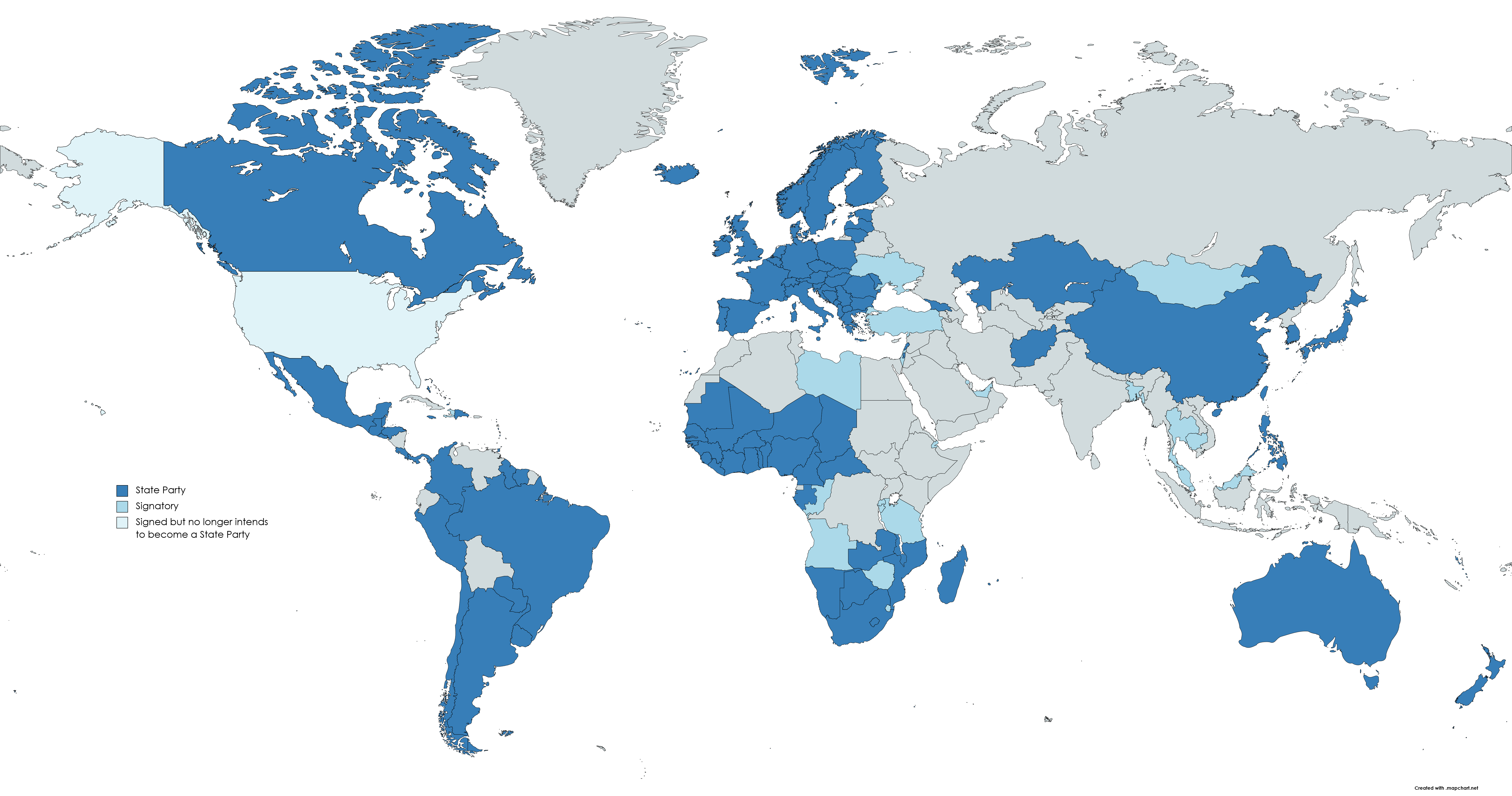
- State Party
- Signatory